Drone sightings around the world represent a rapidly evolving phenomenon with significant implications across diverse sectors. This global increase in unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) observations necessitates a comprehensive analysis of their geographic distribution, operational motivations, regulatory responses, and broader societal impacts. Understanding the types of drones involved, their capabilities, and the contexts in which they are deployed is crucial for assessing both the benefits and risks associated with this technology.
This study examines the frequency and types of drone sightings globally, categorizing them by region and drone model. It explores the diverse motivations behind drone operations, ranging from legitimate commercial and recreational uses to potentially illicit activities, such as surveillance or interference with critical infrastructure. The analysis also considers the evolving regulatory landscape, including national and international efforts to mitigate risks and ensure responsible drone operation.
Finally, the study evaluates the societal impact of increased drone sightings, addressing concerns about privacy, security, and economic implications across various sectors.
Types of Drones Sighted: Drone Sightings Around The World
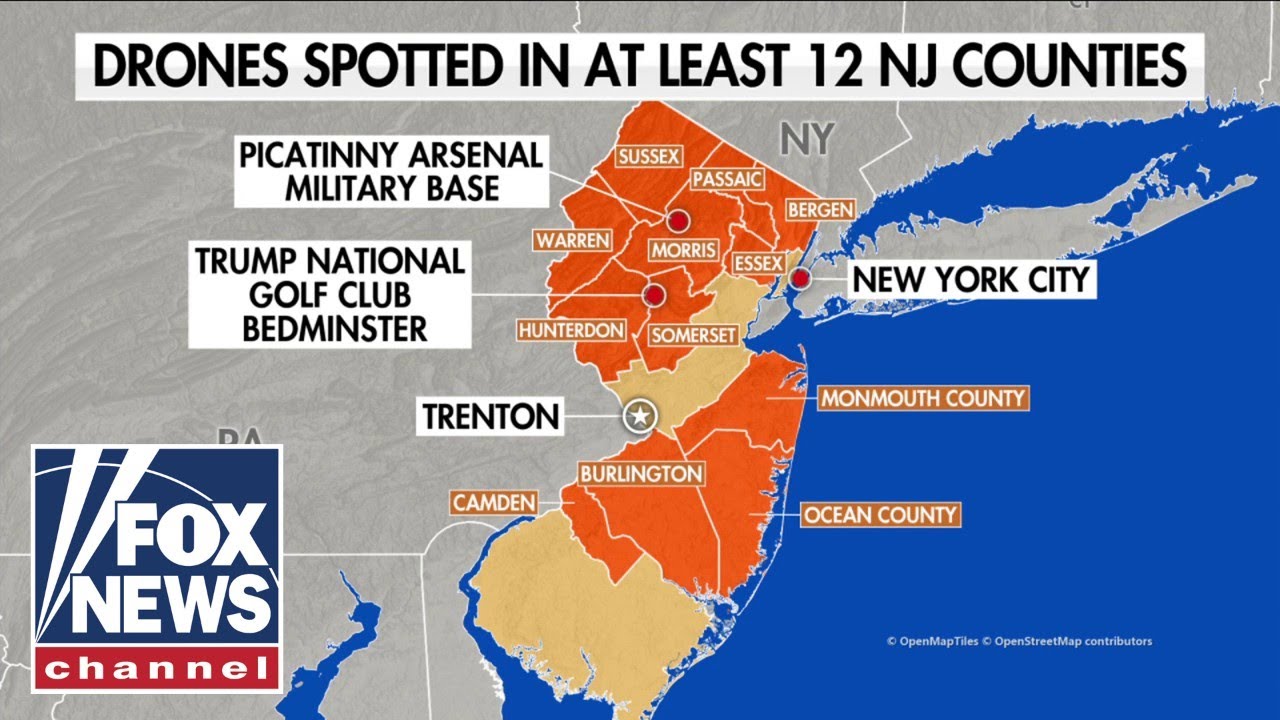
Drone sightings worldwide encompass a diverse range of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), varying significantly in size, capabilities, and intended purpose. Understanding the types of drones observed is crucial for assessing potential risks and implementing appropriate countermeasures. This section categorizes commonly sighted drone models, highlighting their features and capabilities.
Increased drone sightings globally necessitate investigation into various drone types and their capabilities. The recent proliferation includes reports of unusually large unmanned aerial vehicles, some exceeding typical sizes, such as those detailed on the giant drone website. Understanding the technological advancements in larger drone platforms is crucial for analyzing the increasing number of unidentified drone observations worldwide.
Categorization of Commonly Sighted Drone Models
The global proliferation of drones has led to a wide variety of models being used for both legitimate and illicit activities. Categorization can be based on size, capabilities, and intended use. However, visual identification in the field can be challenging, relying often on observed characteristics rather than definitive model identification.
- Consumer-Grade Drones: These are typically small, lightweight quadcopters designed for recreational use, aerial photography, and videography. Manufacturers include DJI (Mavic series, Phantom series), Autel Robotics (Evo series), and Parrot (Anafi series). These drones often feature easily identifiable characteristics such as foldable arms, relatively small size, and readily available consumer-level accessories. Their flight times are generally limited, and their range is typically less than 10 kilometers.
Increased drone sightings globally necessitate improved surveillance and investigative techniques. The recent analysis of footage from a sydney wilson body camera , for example, highlights the potential for such technology to aid in identifying and tracking unauthorized drone activity. Further research into advanced detection systems is crucial to mitigate the growing security concerns associated with unregulated drone operations worldwide.
- Professional-Grade Drones: These are larger and more robust than consumer models, offering enhanced capabilities such as longer flight times, increased payload capacity, and advanced features like obstacle avoidance and precision flight control. Manufacturers include DJI (Inspire series, Matrice series), Yuneec, and others. Professional drones may have distinctive features like interchangeable lenses, specialized sensors, or integrated RTK (Real-Time Kinematic) GPS for precise positioning.
They are commonly used for surveying, mapping, infrastructure inspection, and search and rescue operations.
- Military and Security Drones: These represent the most sophisticated category, often featuring advanced surveillance capabilities, long endurance, and the ability to carry heavier payloads, including weapons. Specific models are often classified, making public identification difficult. However, characteristics such as larger size, stealth design elements, and specialized sensor pods can provide some clues. These drones are frequently used for intelligence gathering, border patrol, and military operations.
Capabilities of Consumer-Grade vs. Sophisticated Drones
A significant difference exists between the capabilities of consumer-grade and more sophisticated drones, particularly those used in security-related contexts. Consumer drones are generally limited in flight time, range, and payload capacity. Their onboard processing power and sensor capabilities are also less advanced. Sophisticated drones, on the other hand, can remain airborne for extended periods, cover vast distances, and carry heavier equipment such as high-resolution cameras, thermal imaging sensors, or even weaponry.
Their onboard processing allows for advanced flight autonomy and data analysis. This disparity in capabilities directly impacts the potential risks associated with their unauthorized operation.
Comparison of Flight Characteristics
The following table compares the flight characteristics of three distinct drone types frequently reported in sightings:
| Drone Type | Speed (km/h) | Range (km) | Max Altitude (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Consumer-Grade (DJI Mavic 3) | 72 | 15 | 6000 |
| Professional-Grade (DJI Matrice 300 RTK) | 80 | 28 | 7000 |
| Military-Grade (Hypothetical Example) | 150 | 200+ | 9000+ |
Note: Military-grade drone specifications are often classified and vary significantly based on specific models and capabilities. The values presented here are estimates based on publicly available information on similar systems.
Motivations Behind Drone Sightings

The proliferation of drone technology has led to a diverse range of operational motivations, encompassing both legitimate and illicit activities. Understanding these motivations is crucial for developing effective regulatory frameworks and security protocols to mitigate potential risks. This section examines the spectrum of drone usage, from beneficial applications to potential security threats.Drone operations are driven by a wide array of factors, reflecting the versatility of the technology.
Legitimate uses frequently involve commercial applications such as aerial photography and videography for construction projects, infrastructure inspections, and agricultural monitoring. Furthermore, drones play a vital role in public safety, contributing to search and rescue operations, emergency response, and law enforcement activities. Conversely, illicit activities involving drones pose significant security challenges.
Legitimate Uses of Drone Technology
The beneficial applications of drones are numerous and expanding rapidly. In disaster relief, drones provide rapid aerial assessments of damage, enabling efficient resource allocation and facilitating search and rescue efforts. For instance, following Hurricane Katrina, drones were deployed to map flooded areas and locate survivors. Similarly, in environmental monitoring, drones equipped with specialized sensors are used to track deforestation, monitor wildlife populations, and assess air quality.
Precision agriculture also benefits significantly, with drones providing farmers with detailed imagery to optimize irrigation, fertilization, and pest control. This leads to increased crop yields and reduced environmental impact. In infrastructure inspection, drones offer a cost-effective and safe alternative to traditional methods, enabling the detection of structural defects in bridges, power lines, and pipelines before they escalate into major problems.
Security Threats from Unauthorized Drone Activity
Unauthorized drone operations near critical infrastructure present significant security risks. The potential for drones to be weaponized or used to deliver explosives to airports, power plants, or other sensitive locations is a major concern. Moreover, drones can be employed for surveillance and reconnaissance, potentially compromising sensitive information or facilitating acts of sabotage. The disruption of air traffic by drones flying near airports poses a direct threat to aviation safety.
For example, the temporary closure of Gatwick Airport in 2018 due to unauthorized drone sightings highlighted the vulnerability of air travel to this emerging threat. Similarly, the potential for drones to be used to disrupt power grids or other essential services underscores the need for robust counter-drone technologies and security measures.
Examples of Beneficial Drone Applications Globally
Numerous examples showcase the positive impact of drones worldwide. In Rwanda, drones are used to deliver blood and medical supplies to remote areas, significantly improving healthcare access. In Australia, drones are employed to monitor the Great Barrier Reef, providing valuable data on coral health and assisting in conservation efforts. In the Amazon rainforest, drones are used to track deforestation and illegal logging activities, aiding in environmental protection.
These examples demonstrate the transformative potential of drone technology across various sectors and geographical locations. The continued development and responsible implementation of drone technology holds the promise of significant societal benefits while necessitating ongoing efforts to mitigate potential security risks.
Regulatory Responses to Drone Sightings

Governments worldwide are grappling with the rapid proliferation of drones, necessitating diverse regulatory frameworks to ensure safe and responsible operation while addressing security concerns arising from unauthorized drone activity. The responses vary significantly depending on a nation’s technological capabilities, existing aviation regulations, and perceived threat levels. A comparative analysis of different national approaches reveals both commonalities and striking differences in enforcement mechanisms and penalty structures.
Comparative Analysis of Drone Regulations in Three Countries, Drone sightings around the world
This section compares and contrasts drone regulations in the United States, the European Union, and China, highlighting key differences in enforcement and penalties. The regulatory landscape is constantly evolving, and these examples represent a snapshot in time.The United States utilizes a tiered system of registration and licensing for drone operators, with stricter requirements for commercial use. Enforcement relies on a combination of federal agencies, such as the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), and local law enforcement.
Penalties range from fines to criminal charges, depending on the severity of the violation. The FAA has established a robust system of airspace restrictions and requires operators to maintain a safe distance from airports and other sensitive areas.The European Union, through its common aviation safety regulations, has implemented a more unified approach across its member states. This involves a system of drone classifications based on weight and risk, with different operating rules and certification requirements for each category.
Enforcement is primarily the responsibility of individual member states, potentially leading to inconsistencies in application. Penalties generally include fines, but the specifics vary across jurisdictions. The EU’s approach emphasizes risk mitigation through a combination of technical standards and operational procedures.China’s drone regulations are largely centralized, with strict licensing requirements and limitations on drone operation in certain areas. Enforcement is rigorous, with significant penalties for violations.
The government’s focus is on national security and maintaining control over airspace, resulting in a more restrictive regulatory environment compared to the US or the EU. Technological solutions, such as drone detection and identification systems, are integrated into the enforcement strategy.
Key Elements of International Agreements or Guidelines Concerning Drone Operation
International cooperation is crucial for addressing the global challenges posed by drone technology. While a single, universally binding international treaty on drones does not yet exist, several key elements are emerging in international agreements and guidelines aimed at promoting safe and responsible drone operation. These efforts often involve collaborations between international organizations such as the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO).
- Standardization of technical specifications: Agreements focus on establishing common technical standards for drone design, construction, and performance, to ensure interoperability and safety.
- Registration and identification systems: Many initiatives advocate for the establishment of global registration and identification systems for drones, facilitating tracking and accountability.
- Airspace management and deconfliction: International collaboration is essential for developing effective mechanisms for managing drone traffic and preventing conflicts with manned aircraft.
- Data sharing and information exchange: Agreements promote the sharing of information on drone incidents, best practices, and technological developments to enhance safety and security.
- Security and counter-drone technologies: International discussions address the challenges of securing airspace from malicious drone use and the development of effective counter-drone technologies.
Technological Solutions for Drone Detection and Tracking
Significant advancements in technology are enhancing drone detection and tracking capabilities. These solutions are critical for addressing both security concerns and ensuring the safe integration of drones into the airspace.Several technologies are being developed and deployed, including radar systems, radio frequency (RF) detection systems, acoustic sensors, and computer vision systems utilizing artificial intelligence. Radar systems can detect drones at longer ranges, while RF systems identify specific drone signals.
Acoustic sensors leverage the sound produced by drone rotors, and computer vision systems analyze video feeds to identify and track drones visually. The integration of multiple sensor types and advanced data analytics improves accuracy and reliability. Furthermore, the development of counter-drone technologies, such as jamming and spoofing systems, provides additional layers of security and control. These technologies are constantly evolving, improving detection range, accuracy, and the ability to identify and neutralize malicious drone activity.
Array
The proliferation of drone sightings globally has engendered a complex interplay of societal impacts, ranging from anxieties surrounding privacy and security to significant economic shifts across diverse sectors. These impacts are multifaceted and require careful consideration to understand their full implications for individuals, communities, and national policies.The increasing frequency of drone sightings has demonstrably influenced public perception and fostered concerns regarding privacy and security.
The potential for unauthorized surveillance, data breaches, and even malicious use, such as the deployment of drones for illicit activities, fuels public apprehension. This is particularly pronounced in densely populated areas and near critical infrastructure. Conversely, the potential benefits of drone technology, such as enhanced security through monitoring and rapid emergency response, are often overshadowed by these concerns, leading to a polarized public discourse.
Public Perception and Concerns Regarding Privacy and Security
Public anxieties surrounding drone technology are fueled by several factors. The unobtrusive nature of drones allows for covert surveillance, raising concerns about potential violations of personal privacy. The capacity for drones to carry payloads, ranging from cameras to potentially harmful materials, raises security concerns, particularly in relation to critical infrastructure, public events, and high-profile individuals. Furthermore, the lack of clear regulations and standardized identification protocols in many jurisdictions contributes to public uncertainty and a sense of vulnerability.
This uncertainty is exacerbated by the ease of accessibility and affordability of drone technology, making it readily available to both legitimate users and potential malicious actors. The resulting public discourse often revolves around balancing the benefits of drone technology with the need to protect individual privacy and national security.
Economic Implications of Drone Use
The economic implications of drone technology are significant and multifaceted, affecting various sectors in both positive and negative ways. While the potential for economic growth through increased efficiency and new opportunities is substantial, challenges related to regulation, infrastructure, and workforce adaptation must be addressed.
| Sector | Benefit | Drawback | Overall Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Delivery Services | Reduced delivery times and costs, expansion into remote areas, increased efficiency. | High initial investment costs, potential job displacement in traditional delivery sectors, regulatory hurdles and safety concerns. | Potentially positive, but requires careful management of transition and mitigation of negative impacts. |
| Agriculture | Precision spraying of pesticides and fertilizers, crop monitoring and yield prediction, reduced labor costs. | High initial investment costs, potential for technical malfunctions impacting crop yields, need for skilled operators. | Potentially positive, offering significant productivity gains, but dependent on technological advancements and appropriate training. |
| Infrastructure Inspection | Reduced inspection costs and risks, improved safety for inspectors, faster inspection times. | High initial investment costs, reliance on reliable network connectivity, potential for data security breaches. | Positive, offering significant efficiency and safety improvements, but requires addressing infrastructure and security challenges. |
| Surveillance and Security | Enhanced security monitoring, rapid response capabilities, cost-effective surveillance solutions. | Potential for misuse, privacy concerns, ethical considerations regarding data collection and use. | Complex, with potential benefits offset by significant ethical and societal concerns. |
Influence on Public Policy Debates
Drone sightings have significantly influenced public policy debates regarding surveillance technology and data privacy. The increasing use of drones by law enforcement and government agencies has raised concerns about potential overreach and the erosion of civil liberties. This has led to calls for stricter regulations on drone use, including requirements for registration, licensing, and data protection. Furthermore, the debate extends to the development of appropriate legal frameworks to address issues such as liability in case of accidents or malicious use, and the ethical considerations surrounding the collection and use of data obtained through drone surveillance.
These debates highlight the urgent need for a balanced approach that fosters innovation while safeguarding fundamental rights and protecting public safety.
The proliferation of drone sightings worldwide underscores the need for a multifaceted approach to managing this increasingly prevalent technology. While drones offer substantial benefits in diverse sectors, ranging from search and rescue to precision agriculture, the potential for misuse and the associated security and privacy risks necessitate robust regulatory frameworks and advanced detection technologies. Further research focusing on the development of effective counter-drone measures and international cooperation on standardization and enforcement is essential to ensure the safe and responsible integration of drones into the global landscape.
Continuous monitoring of drone sightings and their associated contexts will be crucial for adapting policies and technologies to address emerging challenges and maximize the beneficial applications of this transformative technology.
FAQ Explained
What are the most common reasons for drone malfunctions leading to unexpected sightings?
Common causes include GPS signal loss, battery failure, software glitches, and mechanical issues. Environmental factors such as strong winds or precipitation can also contribute.
How are drone sightings impacting insurance industries globally?
Increased drone sightings are leading to higher insurance premiums for infrastructure and high-value assets due to increased risk of damage or theft. New insurance products specifically addressing drone-related risks are also emerging.
What are the ethical considerations surrounding the use of drones for surveillance?
Ethical concerns include potential violations of privacy, lack of transparency, and the potential for misuse by governments or private entities. Balancing security needs with individual rights is a significant challenge.